Bed Bug Biology & Information
What are some common facts I may want to know about the bed bug?
 Bed bugs are small. An adult bed bug can be 3/16 of an inch long or approximately the size of a grain of rice.
Bed bugs are small. An adult bed bug can be 3/16 of an inch long or approximately the size of a grain of rice.- Newly hatched bed bug nymphs can be the size of a pin head.
- Bed bugs are a brownish-red colour when they have ingested a blood meal and an opaque light-cream color when they have not.
- Bed bugs are flat when not fed, and thicker and almost oval shaped when they have had a full blood meal.
- Eggs of a bed bug are nearly impossible to see unless in a severe infestation.
- Bed bugs lay eggs along seams of a mattress and box spring, wooden areas such as bed frames, baseboards, clothing or anywhere the eggs can adhere as they are sticky.
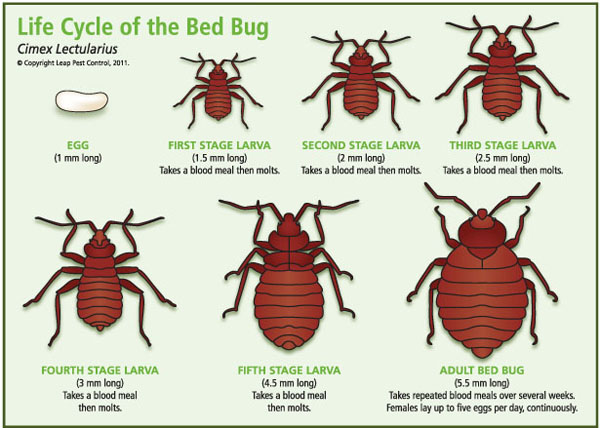
- Bed bugs can lay 1-5 eggs per day. These eggs will hatch between 4 and 12 days.
- Once hatched, the bed bugs must have a full blood meal between each successive molt to advance through each of the 5 nymph stages to become an adult.
- Blood meals can last anywhere from 3-10 minutes long and feed every 5-10 days.
- Bed bugs feed by injecting their elongated beak in to the food source in which they withdraw blood from the host.
- Bed bugs are attracted to the carbon dioxide that we emit and the warmth that the body produces. A bed bug will become active within minutes of human entry to a room and will travel up to 15 feet or more to get to their food source.
- Bed bugs don’t bite in threes. This has become a common myth and is more likely that the bed bug has not found the
proper place to withdraw your blood. Just like a doctor looking for a vein to withdraw blood, the bed bug is looking for that perfect spot on you. - Bed bugs have not been known to transmit disease. Still, bed bugs can harbour pathogens in and on their body, but transmitting diseases is unlikely.
- Bed bug bites can result in an allergic reaction thus setting off a chain of events such as scratching, then becoming an open wound, which can then become infected.
- Bed bug infestation can also cause people mental stress, sleeplessness embarrassment, anxiety and loss of property value.
- Bed bugs can advance through each of these stages to become an adult in as little as 30 days if the conditions are permissible.
- A bed bug nymph can survive without food for up to six months and an adult can survive up to a year without food.
- Infestations generally congregate around the food source, such as the bedroom area, but once the harborage area becomes heavily infested bed bugs will then start to spread to other areas humans spend time like living room or family room.
- A female bed bug once impregnated, can lay eggs for the entire duration of her life.
- Female bed bugs will often leave the congregation after feeding to escape male bed bugs, because the male will continually seek mating and multiply times through traumatic insemination in which the male injects the female through her abdominal wall with his external genitalia. This in effect injures the female and can lead to infection and or death over time. This is why
bed bugs can often be found in other areas of the home.